An elderly Chinese visitor to Jackie French’s home commented with delight on the ‘Golden Hairy Goat’s Testicles’ in the garden, which she hadn’t seen since her childhood. What she was talking about were the kiwi fruit hanging from a vine over Jackie’s pergola. This highly descriptive name the visitor assured her was the name used for the fruit in her village in China.
Although we now use the name kiwi fruit, not so long ago, the plant was better known as Chinese gooseberry. The name kiwi fruit is a marketing name developed by New Zealand growers, which is now used round the world. Kiwi fruit are a widely grown and important export crop in New Zealand.
Details
Common name:
Kiwi fruit, Chinese gooseberry or, if it takes your fancy, golden hairy goat’s testicles. In France it is called the vegetable mouse (souris vegetales).
Botanic name:
Actinidia deliciosa (previously A. chinensis). The genus name Actinidia comes from the Greek meaning ray, alluding to the styles of flowers (the maleflower parts) that radiate like spokes of a wheel.
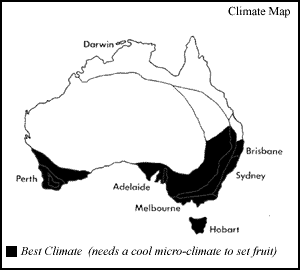
Climate:
Kiwi fruit will grow in all temperate parts of Australia. The main limitation for growth is that fruit requires a minimum of 400-700 hours below 7°C to form fruit. Where winter temperatures do not fall this low, fruit may not form. Extremely high summer temperatures can also affect growth. ( See Climate Map).
Good points:
- The leaves provide summer shade but, as the plant is deciduous, the bare branches allow sun to stream through in winter.
- A vigorous growing vine with delicious sweet fruit in winter.
- Fruit ripens from late autumn to winter (usually around April to June) and can be left to hang on the vine for some time.
Uses:
- Grow over a trellis or pergola around the house to provide shade in summer and allow sun in winter.
- Fruit vine to provide delicious fruit for the home. A strong trellis or fence is needed on which to train the vine for fruit production.
- Kiwi fruit can be eaten whole straight from the skin with a spoon. Alternatively they can be sliced to decorate a pavlova or fruit salad, used to tenderise meat or made into kiwi fruit jam or wine. The skin is not edible.
Likes:
- Sheltered, sunny position in well-drained soil.
- Plants of each sex. To produce kiwi fruit you need a male and a female plant. Only the female plants produce fruit. It is possible to buy plants that have a male and female grafted to the same plant, otherwise you need to grow both the male and the female plant. One male plant will pollinate up to nine female plants. The two can be distinguished when in flower as the female plant, which produces the fruit, has a prominent thick white style in the centre of its flower. This is absent in the male flower. When the plants are not in flower or fruit it is very difficult to tell them apart.
- A sturdy support. The kiwi fruit is shallow rooted and strong growing. Build a strong support in the form of a trellis or pergola.
- Protection from wind. In New Zealand commercial orchards are usually hedged with dense windbreaks to protect the vines.
- Water thoroughly especially in summer as plants can become heat stressed.
Care:
- Kiwi fruit is a hungry plant that grows quickly and crops heavily. It needs regular fertilising. Select Dynamic Lifter, well-composted chook or animal manure, or a complete fertiliser. Fertilise in spring and autumn. Fertiliser can also be applied more frequently during spring and summer if small amounts are given.
- Prune in winter and summer. Prune in summer to keep the vine in check as it is very vigorous. Prune in winter to encourage the formation of new, fruit-producing wood and to remove old, unproductive wood. Remove entire lateral branches every two to three years. Tip: As it is difficult to distinguish the male plant from the female when it is not flowering, prune male plant as soon as it has finished flowering.
Tips on harvesting:
Kiwi fruit can be picked while still hard and taken inside to ripen. Select the largest fruits to pick first. Decide if the fruit is ripe by tasting it. The fruit is sweet when ripe. Note: Kiwi fruit can take up to four years to produce their first crop.
Getting started:
Kiwi fruit vines, including named varieties, are available from selected nurseries throughout Australia. It is necessary to buy a male and a female plant which cost around $12.95 each for a 20cm (8″) pot. Grafted varieties are available but may be difficult to find. Ask your garden centre to order a plant for you.